Quick Screening and Quantitative Analysis of Carcinogens in Medicinal Plants Using DPiMS™-8060
From the viewpoint of preventing health damage, it is necessary to establish rapid and effective screening and quantitation methods for harmful substances which have serious impacts on human health. Harmful substances contained in plants are analyzed by LC and LC/MS, but these techniques require separation using a column and removal of contaminants. Among the problems of these techniques, in addition to the time required for pretreatment and analysis, consumption of organic solvents is also large in some cases.
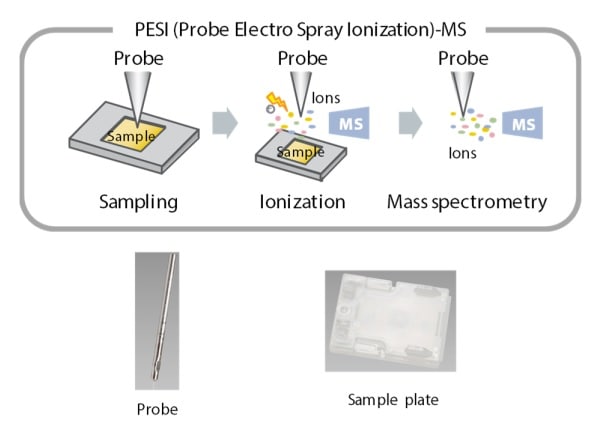
These problems can be solved by the probe electrospray ionization method (PESI), which is one ultra-high speed screening platform supplied by Shimadzu. PESI has already been adopted in analysis of narcotics, pharmaceutical products, pesticides, biotoxins and metabolites.
Aristolochic acid, which is the target of this analysis, is found in plants of the genus Aristolochia, and is classified as a carcinogen, including their plant forms. This article introduces an internal standard method using naproxen for rapid screening and quantitative analysis of four types of aristolochic acid contained in Aristolochia debilis and Asiasarum sieboldii and aristolactam I, which is one of its metabolites, using the Shimadzu DPiMS-8060 direct probe ionization mass spectrometer kit.
Principle of Probe Electrospray Ionization Method
Related Products : DPiMS-8060


